Technicians have come up with an indicator of how well your cows transform feed into milk. Feed efficiency (FE) is the amount of 3.5% fat-corrected milk produced per pound of feed dry matter consumed. The optimal range of feed efficiency is 1.4 to 1.8 pounds of 3.5% fat-corrected milk produced per pound of dry matter consumed[1].
According to the university of Kentucky, different factors impact feed efficiency[2]. Some of them cannot be altered, but others can be manipulated to improve productivity. For example, factors related to health (heath stress, rumen acidosis, somatic cell count) can be improved through an early detection followed by timely intervention and appropriate management practices. Similarly, factors related to diet like additives, forage quality and fiber can be manipulated by an attentive monitoring of feeding behavior and rumination.
What affects feed efficiency?
The study identifies the effects of environmental , health and management factors on feed efficiency :
- Rumen Acidosis: If cows experience subacute rumen acidosis, Feed Efficiency may decrease by 0.1 units.
- Feed Additives: The inclusion of yeast, yeast culture, buffers, or direct-fed microbials in the diet can boost feed efficiency by 0.1 to 0.5 units.
- Forage Quality: Enhanced forage quality enhances feed efficiency, while lower forage quality hampers it. Improved forage quality leads to increased forage intake, digestibility, and subsequently, milk production.
- Fiber Content: As the percentage of NDF (Neutral Detergent Fiber) rises, feed efficiency tends to decline, except when NDF in the total diet reaches 35% and above, at which point feed efficiency remains stable.
- Heat Stress: With an increase in heat stress levels, feed efficiency typically decreases. This decrease can range between 0.1 and 0.3 units, according to the intensity of stress.
A case study : how much milk and money can you save by preventing heat stress?
While automatic monitoring cannot cure cows once they fall ill, it can effectively prevent health issues by promptly detecting anomalies or signs of animal discomfort before they escalate into illnesses or reach critical stages. It can also mitigate the impact of environmental stresses by alerting farmers and helping them to implement protective measures for the herd before health and productivity are negatively impacted. This proactive approach can lead to significant cost savings for dairy farms. For example, in order to mitigate heat stress different practices can be put in place to help cows cope with high temperatures : changing feeding time and feed quality, increase available water, provide shade and ventilation, improve the design of livestock buildings..
The financial benefits on a 100-cows farm
To understand the financial benefits of health and rumination monitoring on feed efficiency and milk production, let’s calculate the value of preventing heat stress in a farm with 100 cows. This calculation focuses on milk production and the revenue it generates. Assuming an optimal feed efficiency of 1.6 (meaning 1.6 pounds of milk for every 1 pound of feed), avoiding heat stress can prevent a reduction of 0.3 pounds of milk per pound of feed. This equates to preventing a 19% loss in milk production. For a Holstein cow producing an average of 75 pounds of milk daily[1], this translates to maintaining 14 pounds of milk per cow each day, that would otherwise be lost because of heat stress.
Given a milk price of $0.196 per pound ([2]), a 100-cow farm can save approximately $274 daily or $1917 weekly by preventing heat stress. This is calculated as 140 pounds of additional milk daily multiplied by the milk price ($0.196), resulting in these significant savings. According to recent research, almost 80% of cattle globally are exposed to heat stress for at least 30 days a year[3]. So, in this hypothetical case, we can estimate the cost savings associated with maintaining milk yield thanks to the prevention of heat stress as 274 x 30 = $ 8220/year.

[1] https://www.holsteinusa.com/holstein_breed/holstein101.html?tab=2#TabbedPanels1
[2] https://www.clal.it/en/?section=latte_usa&type=CL4
[3] North MA et al (2023) Global risk of heat stress to cattle from climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 18 094027
Integrating monitoring data and feed efficiency for a holistic farm management
Information on feed efficiency can be effectively combined with data on rumination and ingestion for informed decision-making aimed at optimizing nutrition and maximizing production over feed intake. The integration of these datasets proves advantageous as it allows for the correlation of deviations in behavioral patterns with changes in feed efficiency, thereby facilitating the identification of underlying causes such as health issues, feed types, or environmental changes.
For instance, if reduced feeding and rumination times are observed without a change in feed efficiency, it may indicate competition within the herd leading to decreased access to feed. Conversely, alterations in both indicators could signify metabolic diseases. The synergy of these datasets enhances the ability to discern the factors influencing herd behavior and productivity.
Farm Life: detecting and preventing feeding and rumination issues for dairy farm success
To facilitate the detection and identification of feeding and rumination-related issues, automatic monitoring tools serve as invaluable allies. They detect abnormal behaviors, integrate various indicators effectively, and ensure comprehensive control within the dairy farm
This advanced approach relies on sensors that continuously collect real-time data, utilizing 3D accelerometers and artificial intelligence algorithms to detect deviations and issue timely warnings to farmers.
FarmLife is a comprehensive solution that uses real time data from sensors mounted on collars. These are combined and analyzed with artificial intelligence to provide a holistic view of cow health status, reproductive performance, rumination, and activity behavior.
If you want to know more about FarmLife, click here.
[1] https://dairy-cattle.extension.org/when-calculating-feed-efficiency-how-do-you-account-for-variations-in-milk-fat-test/
[2] https://afs.ca.uky.edu/dairy/ten-factors-which-impact-dairy-feed-efficiency
Dairy farmers are well aware that cows can exhibit various behaviors when it comes to their eating habits, rumination, and activity levels. These variables affect the quality and quantity of milk and can also inform about the health status of cattle. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor and record cattle behavior meticulously. This allows farmers to predict the impact of events that influence both the quality of milk and beef produced by the cattle.
In the case of freely grazing cows that might be either on pasture or in the barn, it is important to know when grass-feeding actually takes places as opposed to indoor grain feeding. This is because grass and grain feed have different nutritional properties and their proportion in a cow’s diet will affect its health and its production. In modern smart agriculture, data offers the key to enhancing productivity. Tracking these patterns allows to effectively deal with any abnormal changes and any issues or problems can be quickly remedied. By gathering movement, ingestion and rumination data, farmers have the information they need to care for their animals more effectively and adapt nutrition and management.
Real time Monitoring livestock activity makes the difference
In recent years, wireless sensor networks and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies have paved the way for implementing monitoring systems on farms. Accelerometer sensors placed in the cow collar can provide data in real time on the position of cows and their behavior. These systems can analyse ingestion data and cow behavior to estimate the amount of time spent by cows on pasture.
Real time monitoring of cattle grazing behavior reduces the stress of farmers’ daily operations because it allows to have an instant picture of the herd so to
- Optimise livestock productivity: achieving and maintaining cow productivity when using grazing as the primary forage source requires constant management. To know the amount of time spent grazing on pastures at each moment can help farmers to adjust the quantity and quality of indoor feed. This is because when cows are grass-feeding on pastures it is difficult to know exactly how much and how well they are eating. A decreased amount of time spent grazing or longer rumination times can indicate a lack of or low-quality grass available for cows and it might be necessary to supplement indoor rations or transfer cattle to another paddock to preserve milk yield
- Achieve a better milk and beef quality : a careful planification of grazing helps achieve a better quality without hampering productivity. In addition to ensuring productivity, grazing data are useful because they can be used to improve milk and beef quality. Milk and beef from grass-fed cattle are richer in beneficial nutrients such as Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. The healthier nutritional profile of grass-fed milk and beef resonate with consumers that desire natural and sustainable dairy products, and provides additional value to farm production.
- Optimize pasture management: Identifying the optimal time to move the herd from one paddock to another is key. Grazing & pasture management aims at achieving the benefits of fresh grass without harming the long term growth & nutritional quality of the pasture. Knowing how much grazing takes place helps implement good practices such as dynamic rotational grazing and other techniques aimed a maximising grass-feeding benefits.
- Promote animal welfare : grazing is a livestock practice that is in very high demand by society and consumers concerned about animal welfare. Scientific research shows that pasture access can promote natural behavior, improve health, and given the choice cows tend to spend most of their time outside. However, livestock breeders need to be watchful because grazing cow welfare depends on a number of conditions: water needs to be plentiful and accessible, unhealthy animals need to be taken care of, outdoor diseases (insect-borne, bacterial) need to be prevented and the availability of good quality forage needs to be verified. For all these reasons, monitoring tools for cattle can help farmers to take measures to maximise the health benefits of grass-feeding while keeping an eye on risks.
- Maintain nutritional balance and improve reproduction : To be aware of the amount of grass vs grain ingested at any time by grazing livestock allows farmers to adjust rations in order to optimize and maintain an adequate nutritional balance and ensure that enough food is available to cows. Nutritional balance results in a healthier herd decreasing health expenses and improving reproduction

Grass’live®: create your grazing calendar with an automatic monitoring tool for grazing livestock activity
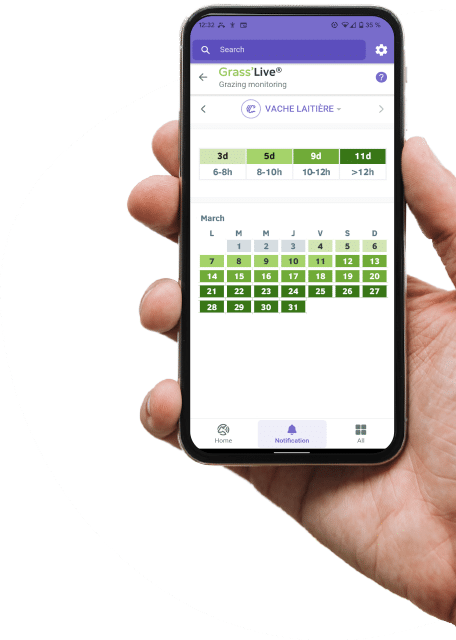
Thanks to the FarmLife monitoring all-in-one solution, real-time monitoring of grazing behavior has become a reality with the introduction of Grass’live®. This innovative service offers a 7-day grazing calendar, enabling farmers to ensure traceability, adjust herd management strategies, and achieve the production of premium quality meat and milk.
Grazing days are obtained automatically through the analysis of data from the accelerometer on the cow collar. The service estimates the time spent on pasture by the group based on the feed intake at the trough and the feed intake at pasture of the animals in the group. This requires data from a group of at least 5 cows, as it returns collective statistics which are displayed on a calendar, which can be edited and downloaded. The information on the calendar includes
- the days spent on pasture
- the time spent on pasture for each of these days.
- the cumulated number of pasture days during the year.
Organic and grass-fed certification made easy
Grazing is a livestock practice that is in very high demand by society and consumers concerned about animal welfare. In today’s market the advantage of grass fed dairy and beef becomes more and more evident, and farming systems which have evolved to maximise production from grass with little reliance on other feed types are rewarded.
In Europe (UK, Ireland, Germany etc) and the US, different grass-fed standards have recently has been developed, in response to the demands of the marketplace. Increasingly purchasers are expressing a desire for dairy products displaying a grass-fed certification. It is no longer acceptable to just declare that a product is Grass Fed, the market requires evidence to support the claim.
With Grass’live® within Farmlife this evidence is easily provided, thanks to the automatically generated grazing calendar.
Track the behavior of cows wherever you are, with your smartphone or tablet
The Grass’live® service within Farmlife integrates the already existing services to monitor ingestion, reproduction, heat and cow activity. It is easy to install within 15 minutes and does not demand any maintenance. With Grass’live® farmers can access information on the grass-feeding activity of their herd at any time, through their smartphone, tablet, or computer:
- Access to data on cow presence on pasture for the previous days.
- For each group of animals, identify the days and time spent on pasture
- Check and compare grass intake patterns and trends over the last 7 days.
- Quickly access the total number of grazing days in the year.Traceability. All rumination data are stored. Keep a history of the past two years
- To compare changes from year to year.
- Access, upload and edit an automatically generated grazing calendar
- To reduce administrative workload. Easily transfer data